American expat Sarah Johnson moved to Stockholm for a tech job at Spotify. She discovered her US citizenship created unique tax challenges. Her Swedish colleagues paid only local taxes. Sarah faced dual filing requirements across two continents.
Introduction to Tax Residency and Obligations
Understanding Tax Residency in Sweden
Sweden considers you a tax resident after six months of continuous stay. The Swedish Tax Agency (Skatteverket) uses center of vital interests tests. These include family location and economic ties. Permanent housing and family presence strongly influence residency status. Tax residents pay Swedish tax on worldwide income. Non-residents pay tax only on Swedish-sourced income.
Key Tax Obligations for US Citizens
US citizens must file taxes regardless of residency. The IRS requires worldwide income reporting. Americans abroad face Foreign Bank Account Reporting (FBAR) requirements. Accounts exceeding $10,000 must be disclosed annually. Failure to file can trigger severe penalties. The IRS pursues non-compliant taxpayers aggressively.
Tools
Call home for less
Save up to 90% on international calls to family and friends.
Links may be monetized via affiliate partners.
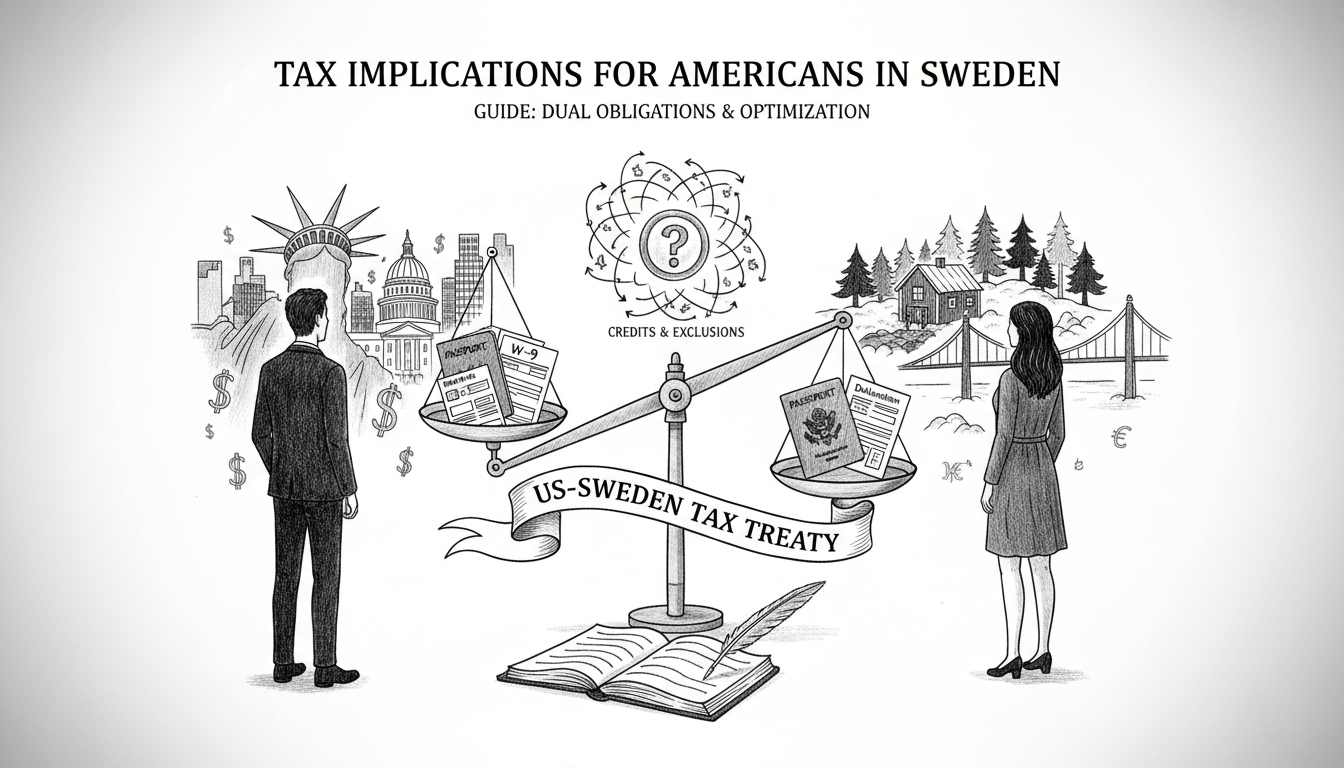
Navigating the US-Sweden Tax Treaty
Overview of the Tax Treaty Provisions
The 1994 US-Sweden tax treaty determines taxing rights. It covers income taxes for individuals and corporations. Treaty provisions override domestic law in conflicts. The treaty defines permanent establishment rules. It specifies which country taxes specific income types. Capital gains and dividend taxation follow special rules.
How the Treaty Prevents Double Taxation
The treaty uses exemption and credit methods. Sweden typically exempts certain US-sourced income. The US provides foreign tax credits for Swedish taxes paid. Americans can claim credits against US tax liability. The Foreign Earned Income Exclusion offers another option. This excludes up to $120,000 of foreign earnings from US tax.
Filing Requirements and Deadlines
Swedish Tax Return Process
Swedish tax returns are due May 2 annually. Most taxpayers receive pre-populated forms from Skatteverket. The agency calculates taxes using PAYE system data. Taxpayers verify information online via Skatteverkets e-tjänst. Corrections require supporting documentation. Final tax bills or refunds arrive by November.
US Tax Filing Deadlines and Extensions
US expats file Form 1040 by April 15 automatically extended to June 15. Further extensions to October 15 are available upon request. FBAR filings (FinCEN 114) are due April 15 with automatic extension to October 15. Streamlined Compliance Procedures help previously non-compliant taxpayers avoid penalties.
Common Tax Scenarios and Strategies
Reporting Income from Employment and Investments
Stockholm-based engineer Mark earns 750,000 SEK annually at Ericsson. He reports this income on both Swedish and US returns. His Swedish ISK investment account generates 50,000 SEK in gains. Mark reports these on Form 8949 and Schedule D. He uses IRS Form 1116 for foreign tax credits. This avoids double taxation on already-taxed income.
Utilizing Foreign Tax Credits and Exclusions
Foreign Tax Credits require meticulous calculation. Credits cannot exceed US tax on foreign income. The $120,000 Foreign Earned Income Exclusion reduces taxable income. Housing exclusion covers reasonable foreign housing costs. Choosing between credits and exclusions requires professional analysis. Most Americans in Sweden benefit from credit method.
Practical Tips for Compliance and Savings
Keeping Accurate Records and Documentation
Maintain seven years of tax records digitally. Use Expensify for receipt tracking costing $5 monthly. Store documents in Google Drive or Dropbox. Keep separate folders for Swedish and US documents. Document currency conversion rates for all transactions. Save all Skatteverket correspondence and tax assessments.
Seeking Professional Tax Advice
Hire specialists familiar with both systems. Greenback Expat Tax Services charges $400-$800 for expat returns. Stockholm-based firm JMW Konsult offers bilingual services. Schedule consultations in October for year-end planning. Verify advisor credentials with IRS Directory. Ask for client references from other American expats.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if I miss US tax filing deadlines?
File immediately using Streamlined Foreign Offshore Procedures. These eliminate penalties for non-willful late filing. You must file three years of tax returns and six years of FBARs. The process typically takes 4-6 months. Professional assistance costs $2,000-$4,000.
Do I pay US social security taxes while working in Sweden?
The US-Sweden Social Security Agreement determines payments. Americans on temporary Swedish assignments often pay US social security. Long-term residents typically pay Swedish social security contributions. This avoids dual social security taxation.
How are Swedish retirement accounts treated for US taxes?
Swedish ISK and kapitalförsäkring accounts create US tax complications. ISK annual taxes qualify for foreign tax credits. Kapitalförsäkring policies may be PFICs requiring complex IRS Form 8621. Many advisors recommend avoiding Swedish investment wrappers.
Can I deduct Swedish mortgage interest on US taxes?
US taxpayers cannot deduct foreign mortgage interest. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act eliminated this deduction for non-US properties. Swedish mortgage costs remain deductible on Swedish tax returns. This creates permanent differences between the two systems.
What Swedish tax forms do Americans need?
Request Swedish tax return (Inkomstdeklaration 1) from Skatteverket. Employers provide income statement (Kontrolluppgift). Keep all tax assessment notices (Slutlig skattebesked). Bank statements show capital income and account balances. These documents support US foreign tax credit claims.
How does Swedish wealth tax affect Americans?
Sweden abolished national wealth tax in 2007. Some municipalities imposed temporary wealth taxes subsequently. Americans must report worldwide assets for US tax purposes. The US imposes no wealth tax currently. State-level property taxes apply to real estate holdings.
What happens to my US retirement accounts while living in Sweden?
Traditional IRA and 401(k) accounts continue growing tax-deferred. Roth accounts remain tax-free for qualified distributions. Swedish tax treatment varies by account type. Most US retirement accounts receive favorable Swedish treatment. Consult cross-border tax specialists for specific advice.